ITT AN/ALQ-136 Countermeasures Processor – Bit Slice with a Bite
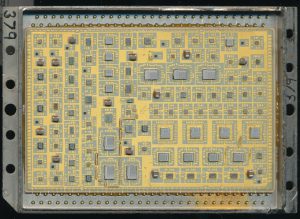
ITT 80063SM-A-919797 – AN/ALQ-136(V)I Processor. The 2901B’s are the 4 larger dies in a row, middle right.
Military computing applications require many custom designs, as they are very mission specific. A great example is this ITT hybrid processor. It was designed and used for the AN/ALQ-136(V)1 CMS (CounterMeasures System) for the AH-1F Cobra Attack helicopter. Two of these hybrids are used in the system, one for the Mod Recovery board, and one for the SLO processor board. These boards are used to detect hostile pulse RADAR systems, analyze them, and begin jamming based on what type they are.
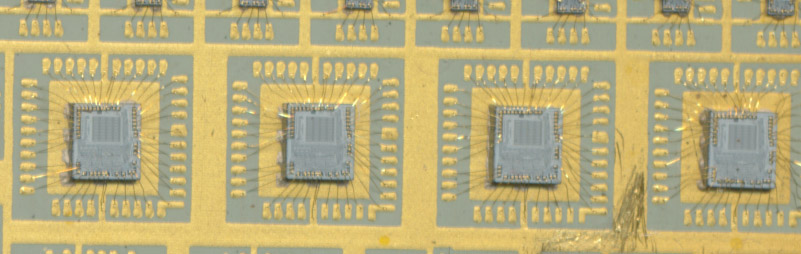
This requires relatively fast processing, and a generally custom design. Today a modern DSP processor could handle this task without issue. However in the early 80’s (the AN/ALQ-136 debuted in 1982) DSP processors were in their infancy. In 1982 a fast custom processor needed to be built with bit-slice elements. In this case the very versatile AMD 2901 was used. The ITT hybrid integrates 4 AMD AM2901B processor dies, as well as associated memory and interfacing elements. The single package contains almost 100 dies, and many discrete components. It is built on a ceramic substrate with gold traces, and sealed in a metal package. This is required to protect the digital components of the system from electronic interference, whether from external sources, or from the helicopters own RADAR systems. The AN/ALQ-136 is designed to prevent the Cobra from being successfully targeted by RADAR guided missiles, failure means a strong possibility that the helicopter gets hit, not something its crew would like to deal with.
The 4 AMD 2901Bs run at 16MHz (50% faster then the original 2901s) and are made with ECL; together they provide 16-bit processing of the incoming RADAR signals. The SLO (Side Lobe Opposition) and MOD Recovery (Modulation Recovery) are used to determine the exact type of the enemy RADAR. Each RADAR has a distinct characteristic that the CMS can match and respond to. The CMS is programmed to respond to the radar signals of the most critical threat weapon systems anticipated to be encoun
tered in the hostile environment. These signatures are stored in the hybrids ROMs as well as the desired response to them. Updates likely remain replacing these hybrids with updated versions. New countermeasures systems (such as the 136’s replacement, the AN/ALQ-211) are more easily upgradeable to new threats.
The AH-1F Cobra continues to fly with the air forces of several countries around the world, notably Pakistan, Jordan, and Turkey. The United States Forest Service also operates 25 AH-1F Cobras for wildland fire use, but it is rather unlikely that the countermeasures on these are operable, let alone needed.